News

09 October 2025
2025 Lab Coat Ceremony Welcomes Graduate Students To Their Thesis Labs
An annual tradition marks the start of scientific discovery for the 2024-2025 class of Stowers Graduate School students.
Read Article
News
Memories of “firsts”—a first kiss, first love, first heartbreak—feel permanent. But why do we remember some moments yet forget others?

The intricate mesh of neurons within the brain of a snail. Image courtesy of Carlos Barradas Chacon, Sánchez Alvarado Lab
By Rachel Scanza, Ph.D.
Memories of “firsts”—a first kiss, first love, first heartbreak—feel permanent. But why do we remember some moments yet forget others? And how do diseases like Alzheimer’s and frontal lobe dementia make memories gradually disappear entirely?
The Stowers Institute for Medical Research is addressing both memory formation and its relentless regression with age.
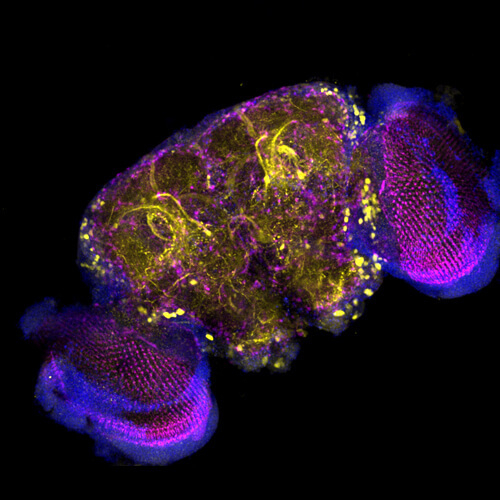
In this adult fruit fly brain imaged on a confocal microscope, sweet-sensing neurons are seen in yellow, while magenta shows the neuronal connections. Image courtesy of Consuelo Perez Sanchez, Jeffrey Lange, Christopher Wood, John Bestor, Si Lab
Understanding why and how we are able to maintain some memories but not others is the focus of Stowers Scientific Director Kausik Si, Ph.D.
Of the approximately 86 billion neurons in the human brain and the hundreds to thousands of synapses associated with each cell, trillions of messages are continuously sent and received. Within these synapses, the Si Lab has discovered that proteins group together to support the maintenance of a memory.
This physical substance for memory storage, termed “functional amyloid,” is a perfect rendering of the amyloids associated with brain diseases and memory loss.
Memory is extraordinarily complex. However, scientists typically
classify different aspects of memory: time duration, qualitative type
(conscious or unconscious), and quantitative kind (rewarding or
punishing).
Sensory, working, and short-term memories persist for very brief
periods of time, ranging from less than a second to around a minute. Some of these can be converted to long-term memory, although the mechanisms are mystifying. Long-term memory, which can stick around indefinitely, is correlated with the synthesis of new proteins and synaptic connections.
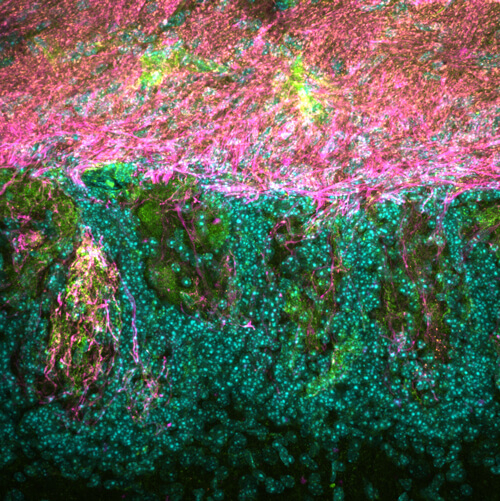
Nerve fibers in the mouse olfactory bulb are highly organized. Fluorescent labeling helps scientists visualize individual nerve fibers and their precise arrangement and connections within the nervous system. Image courtesy of Jae Hyoun Seiler, Yu Lab
Most memories begin from a sensory experience yet nearly all memory can be categorized as either explicit or implicit, meaning conscious or unconscious. Explicit memories are those we deliberately took the time and effort to form, like memorizing a piece of music or your phone number. Implicit memories like learning to play an instrument can be deliberate as well but are not consciously retained. The age-old adage, “It’s like riding a bike,” is a prime example.
Different types of memories are stored within multiple structures of the brain. The amygdala stores emotional responses like fear. The hippocampus is where explicit memories are located, while the striatum houses those implicit bike-riding skills. Additionally, the temporal lobes and hippocampus play a variety of roles in forming and recalling memories.
Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, ALS, frontal lobe dementia, and Alzheimer’s are just a handful of neurogenerative diseases that cause memory loss. They all share the accrual of stable protein clumps within the brain that are associated with toxicity and neuronal cell death, and it is this slow accumulation that accounts for the progressive nature of dementia.
The exact causes for Alzheimer’s, the most common form of dementia, are aggressively debated. There appears to be some component that is genetic—particularly for the early-onset form—yet environmental factors including lifestyle and education can raise or lower one’s risk of developing the disease.
While most other forms of dementia do not seem to have a concrete correlation with genetics, unique among them is Huntington’s which is a focus of Associate Investigator Randal Halfmann, Ph.D.
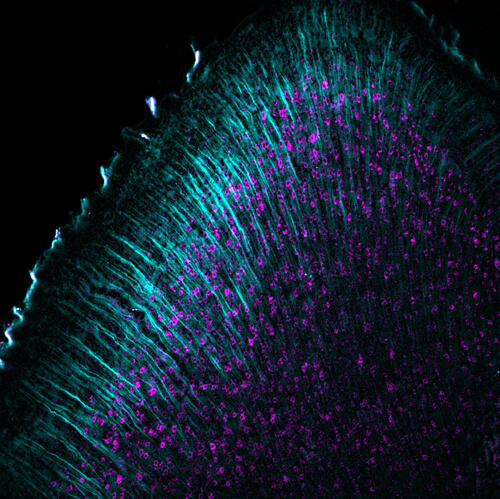
Neurons in the outer part of the mouse brain (cortex) revealing a protein that is important for memory formation (cyan) and cell nuclei (magenta). These cells stretch across a large part of the brain with long, thin projections (lines in cyan). Image courtesy of Mary Huff, Olivia Lawler, Hannah Wilson, Jeffrey Lange, Si Lab
Not only does it have a strong genetic basis, the number of the repeated amino acid, glutamine within pathologic huntingtin protein, precisely determines the age at which an affected individual would die of the disease.
Memory can be monstrously unfaithful. While certain memories seem to be ingrained in our very sense of identity, other very memorable experiences frequently disappear. To discover why, the Si Lab is investigating whether the departure of a memory is associated with the dissolution of the amyloid substrate that secures it.
The seemingly random formation or dispersal of amyloid, whether functional or pathogenic, may yet reveal itself to be a tightly regulated process.
News

09 October 2025
An annual tradition marks the start of scientific discovery for the 2024-2025 class of Stowers Graduate School students.
Read Article
In The News

17 September 2025
From New Scientist, Inflammation is a vital part of the immune response, but it seems that the system can sometimes go awry, resulting in chronic inflammation that has been linked to conditions such as cancer.
Read Article
News

29 July 2025
"Most of my best ideas—and opportunities—came from conversations with other scientists. Share data, workshop problems, collaborate. It’s the single most valuable habit I’ve cultivated."
Read Article